Object Detection with YOLO Part 3 (Integration with ROS, WSL2 Ubuntu 18.04)
Introduction
In this post, I tried integrating YOLO with ROS on Ubuntu 18.04 via WSL2.
This setup is commonly used in robotics to detect objects with YOLO and then move the robot to the detected positions. Since object detection happens in real-time, it pairs perfectly with robotics.
I built the necessary environment and tried out the sample programs provided by Ultralytics.
▼I had been using an Ubuntu 18.04 environment I built previously, but things got complicated, so I reinstalled it to verify the steps from scratch.
▼Previous articles are here:
Starting the Camera
▼I am using a gaming laptop purchased for around 100,000 yen, running Windows 11.
Originally, I wanted to use the USB camera I set up last time, but I couldn't resolve the lag issues.
Fortunately, I was able to borrow an Intel RealSense D435, so I used that for this project.
▼This camera is also capable of depth measurement. I plan to look into its features more deeply later.
The procedure for connecting the camera to the WSL2 environment is the same as in my previous article.
▼Please refer to this article for connection details:
I installed the necessary packages to use the D435.
▼I referred to the following page:
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/realsense-ros/tree/ros1-legacy
Since I am running in a ROS Melodic environment, I specified melodic. Please change this according to your environment.
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-realsense2-cameraI started the camera with the following command:
roslaunch realsense2_camera rs_camera.launch▼If the camera permissions haven't been changed with chmod, an error saying "The requested device with is NOT found" appears. Also, no ROS Topics related to the camera were available.
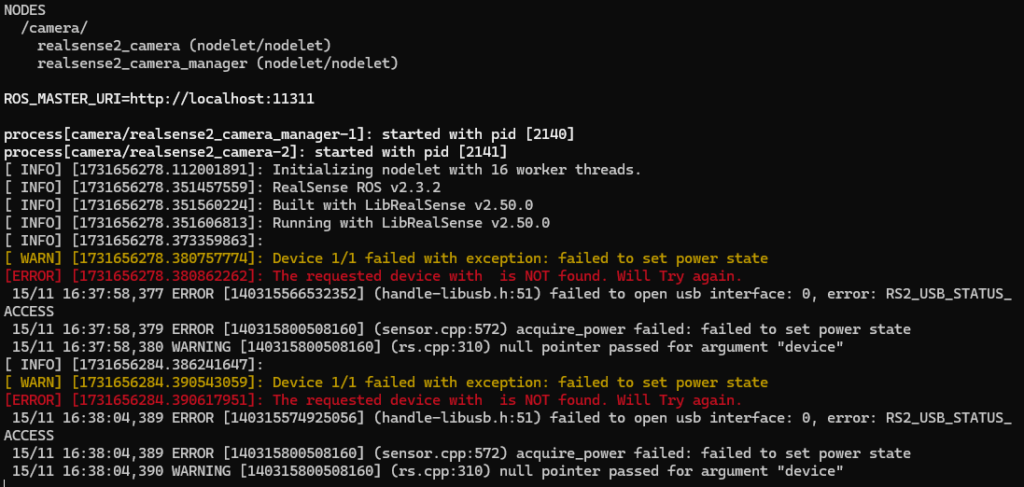
▼Please check and change the permissions following the steps in my previous article.
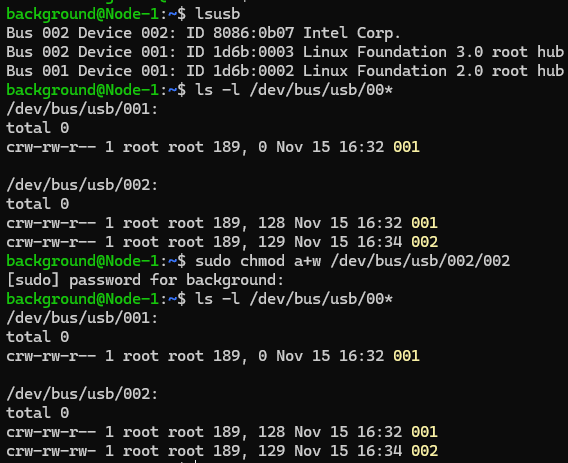
▼When running correctly, no errors were shown.
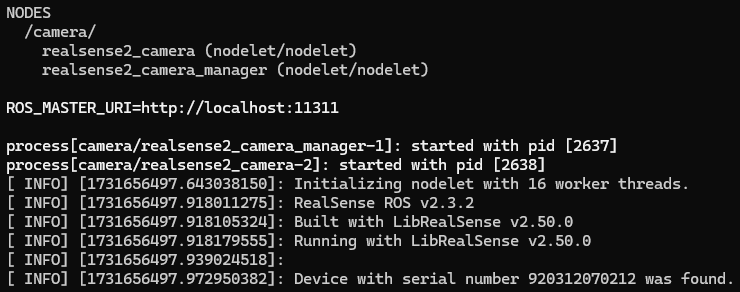
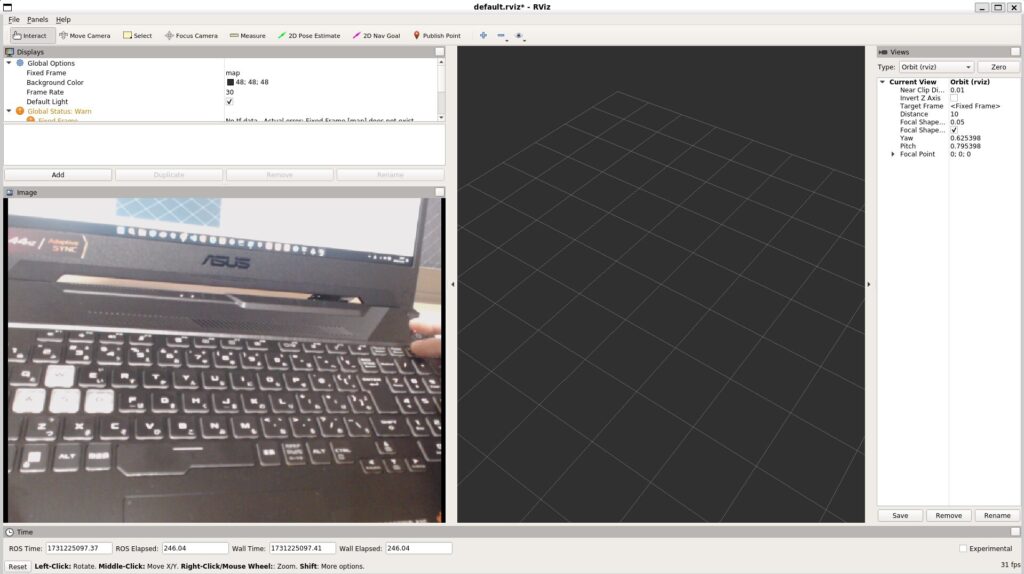
Next, I ran rviz to check the camera footage.
▼Select Add on the left side and choose the topic.
▼Under the /camera section, there are /color and /depth.
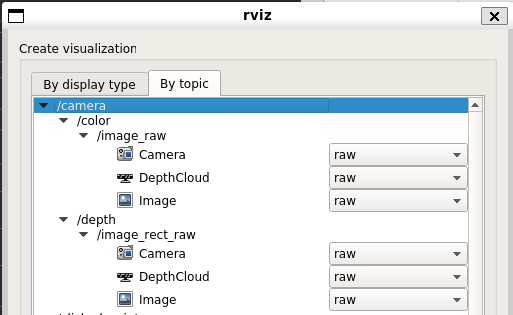
I selected Image under /image_raw for each to check the camera feed.
▼The camera footage was displayed successfully.

Building the YOLO Environment
I tried to install ultralytics via pip, but it seemed like the Python version was not supported.
▼The version of python3 is 3.6.9.
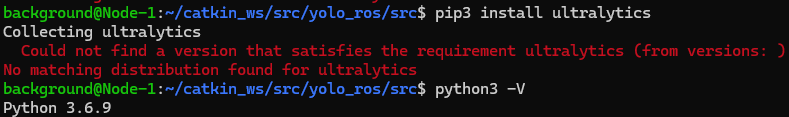
▼By the way, the version for the python command is 2.7.17.
Upon researching, I found that Ultralytics YOLO is compatible with Python 3.8 to 3.12.
▼It was mentioned on the following page:
https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics
I had previously used YOLO in a Windows environment with Python 3.8. I decided to install Python 3.8 on Ubuntu 18.04 and try it out.
I installed the necessary components using the following commands:
sudo apt install python3.8
sudo apt install python3-pip
python3.8 -m pip install -U pip
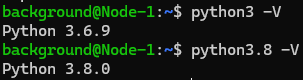
python3.8 -m pip install ultralytics▼Checking the version with python3.8 -V confirmed it was 3.8.0.
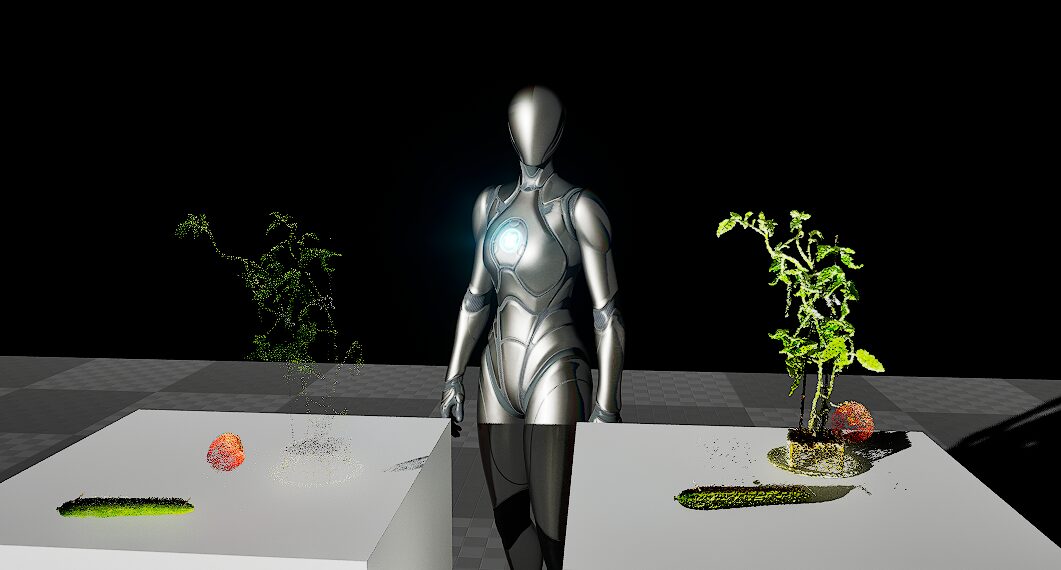
I tried detection using an image from Unreal Engine 5, which I also used in my previous YOLO article.
▼I'll use this image.

I downloaded the image and created a program using the following commands:
wget https://404background.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/unreal.jpg
sudo nano yolo_test.pyI wrote the following code—a simple program that loads the model and outputs the detection results:
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
results = model("unreal.jpg")python3.8 yolo_test.py▼The detection results were output!
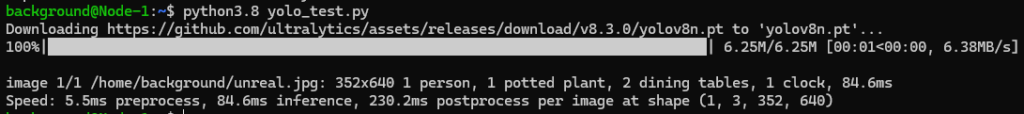
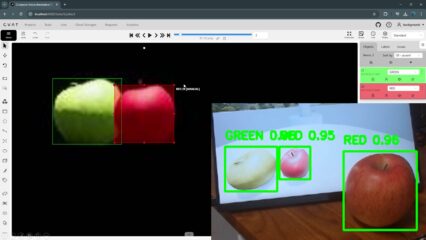
Just like last time, "1 person, 1 potted plant," etc., were detected.
Creating the ROS Package
There is a project called YOLO ROS that uses YOLO v3, which was used on robots in my laboratory. This time, I am integrating Ultralytics YOLO v8 with ROS using a different method.
▼The YOLO ROS page is here:
https://github.com/leggedrobotics/darknet_ros
I'll create a package for YOLO.
▼Regarding Python package creation, I've tried simple code in a previous article.
I used the following commands to create the package and write the program:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
catkin_create_pkg yolo_ros std_msgs rospy roscpp sensor_msgs
cd yolo_ros/src
sudo nano yolo_ros.py▼For the program, I used the ROS sample code provided by Ultralytics:
https://docs.ultralytics.com/guides/ros-quickstart
I wrote the following code in yolo_ros.py. Only the first line is different.
#!/usr/bin/python3.8
import time
import ros_numpy
import rospy
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from ultralytics import YOLO
detection_model = YOLO("yolov8m.pt")
segmentation_model = YOLO("yolov8m-seg.pt")
rospy.init_node("ultralytics")
time.sleep(1)
det_image_pub = rospy.Publisher("/ultralytics/detection/image", Image, queue_size=5)
seg_image_pub = rospy.Publisher("/ultralytics/segmentation/image", Image, queue_size=5)
def callback(data):
"""Callback function to process image and publish annotated images."""
array = ros_numpy.numpify(data)
if det_image_pub.get_num_connections():
det_result = detection_model(array)
det_annotated = det_result[0].plot(show=False)
det_image_pub.publish(ros_numpy.msgify(Image, det_annotated, encoding="rgb8"))
if seg_image_pub.get_num_connections():
seg_result = segmentation_model(array)
seg_annotated = seg_result[0].plot(show=False)
seg_image_pub.publish(ros_numpy.msgify(Image, seg_annotated, encoding="rgb8"))
rospy.Subscriber("/camera/color/image_raw", Image, callback)
while True:
rospy.spin()The first line was written as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python3.8▼I specified this because python3.8 was located in the /usr/bin/ folder.
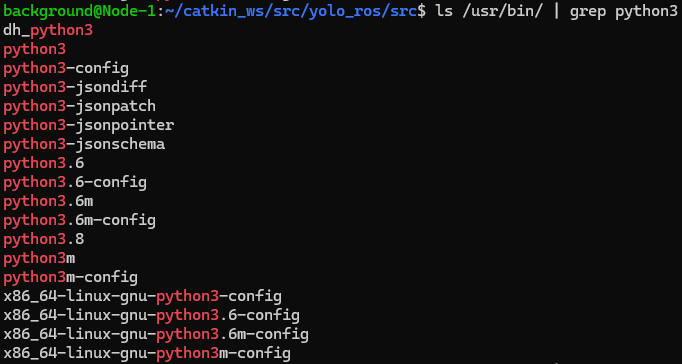
▼When I forgot this first line (called a shebang), I encountered an error saying "import: command not found." Since yolo_ros was not auto-completing with Tab, I think it wasn't being recognized as a package.
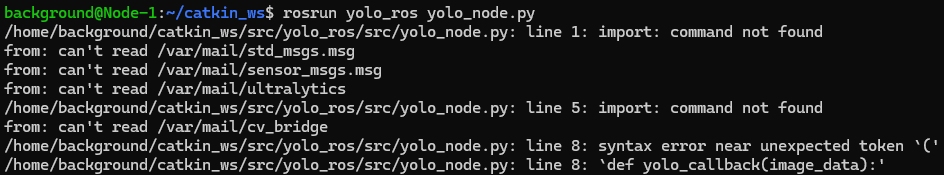
I changed the permissions for yolo_ros.py and ran catkin_make.
sudo chmod 755 yolo_ros.py
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make▼Without running chmod, it wasn't being recognized as an executable file.
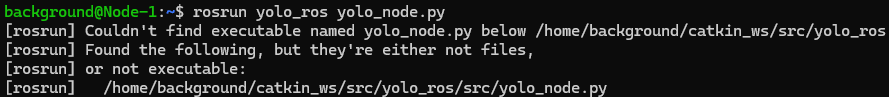
▼No errors occurred.
I tried running the command to execute yolo_ros.py.
rosrun yolo_ros yolo_ros.py▼An error appeared saying "ros_numpy" is missing.
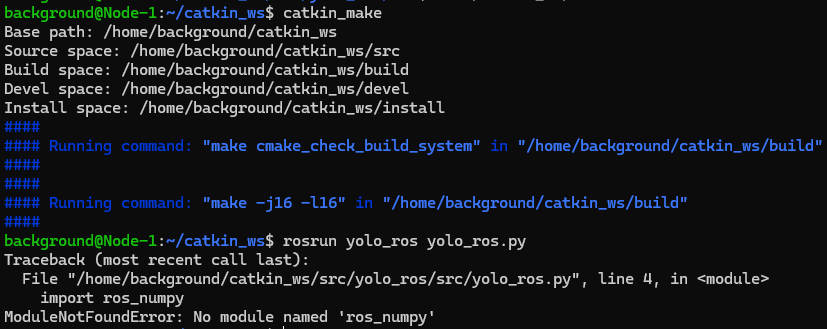
I tried installing it with pip install ros_numpy, but errors occurred, so I tried several things like downloading from GitHub.
▼It cannot be downloaded as "ros_numpy".
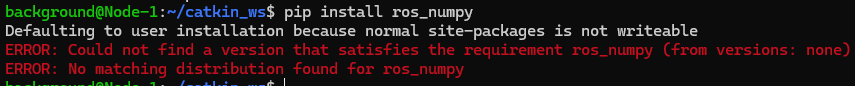
However, checking the ros_numpy page, the installation command was actually pip install rosnumpy. This was a bit of a tricky point for me personally.
▼This is the page:
https://pypi.org/project/rosnumpy
After installing rosnumpy and running the command again, it then said "rospkg" was missing.
▼I was able to install this easily with pip install rospkg.
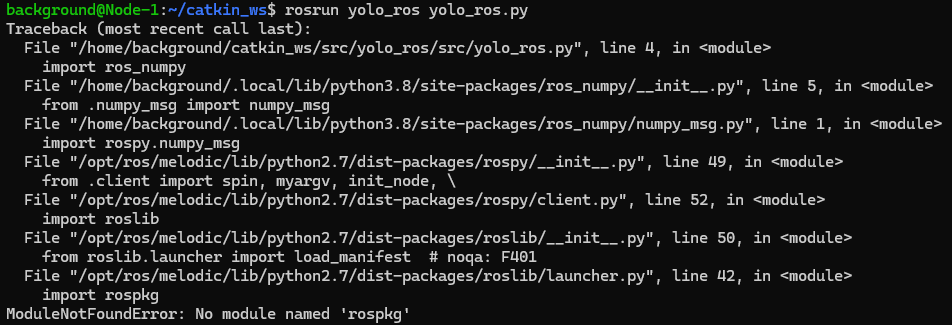
Running the command yet again, an error appeared saying "netifaces" was missing.
▼Looking at the error, it seems netifaces was being called by Python 2.7. I handled this using pip for Python 2.7 instead of Python 3.8.
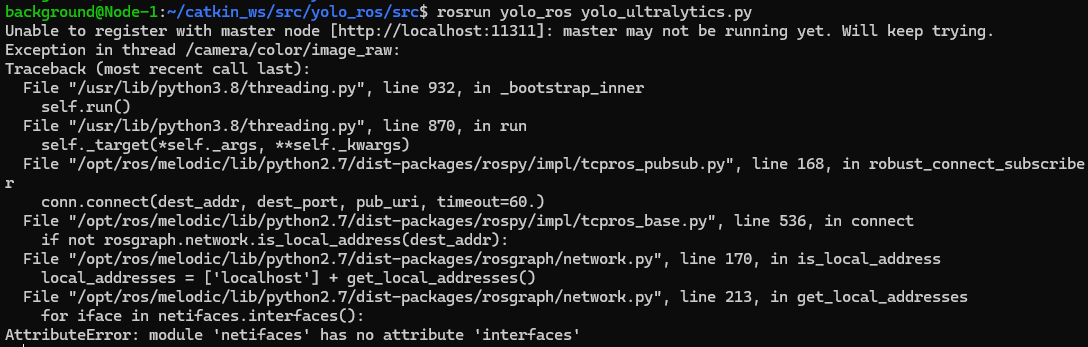
It seemed it was already installed, but upgrading it with the following command increased the version.
pip install -U netifaces▼The version increased from 0.10.4 to 0.11.0.
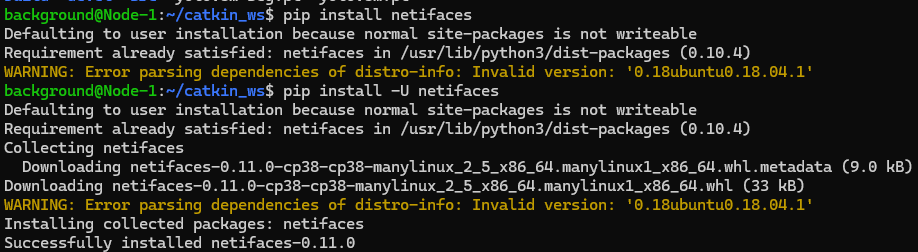
In this state, I was able to run the command successfully.
Running the System
Now that everything was ready, I restarted all the necessary components. If you want to restart the WSL2 environment, running "wsl --shutdown" in PowerShell will stop it.
I ran roscore and allowed the camera footage to be used in a new terminal.
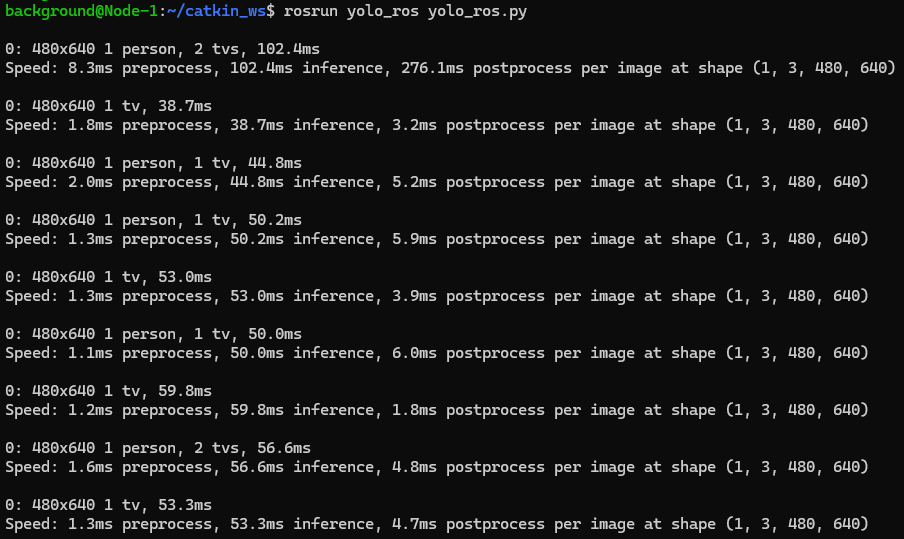
roslaunch realsense2_camera rs_camera.launchThen, I opened another terminal and executed YOLO.
rosrun yolo_ros yolo_ros.py▼It might take some time to start initially, but the detected objects were output as follows:
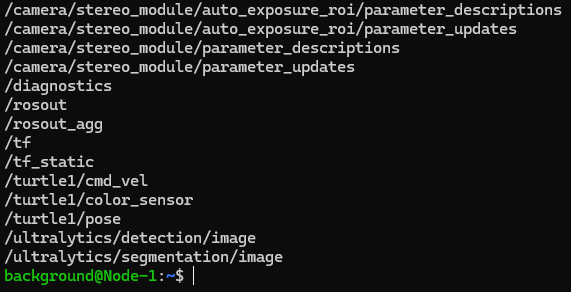
I opened yet another terminal and ran "rostopic list" to check the topics.
▼There are /detection and /segmentation under /ultralytics.
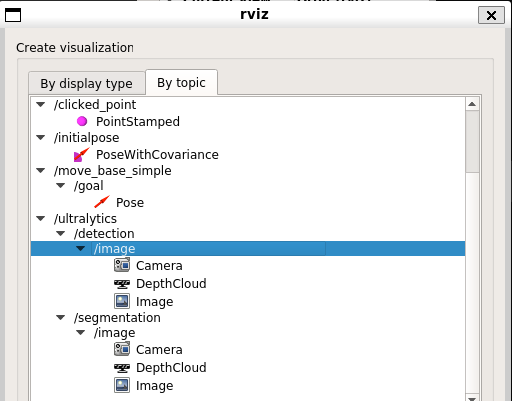
I checked the results in rviz.
▼/detection and /segmentation for /ultralytics are also here.
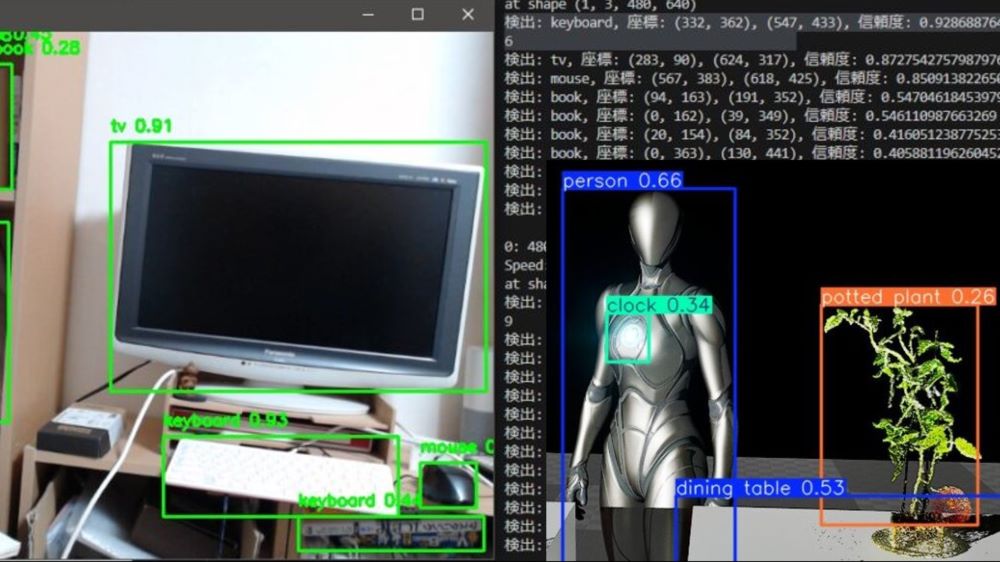
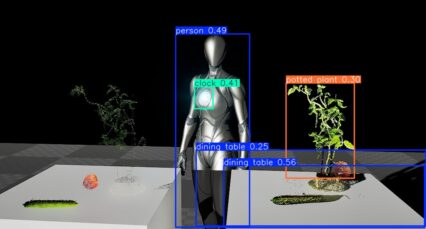
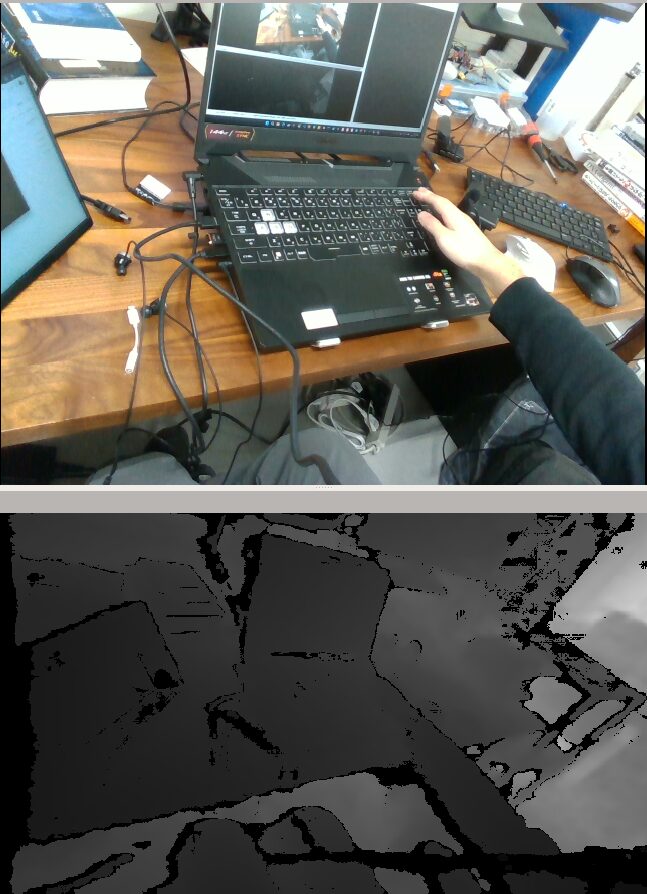
I recorded what was actually displayed in RViz.
▼Since I could only display the RViz window on the left, the camera feed is small.
▼I confirmed that object detection and semantic segmentation were being performed.

Finally
I didn't dwell on it too much, but dealing with Python versions and package issues was quite a struggle. Although I verified the steps by uninstalling the Ubuntu environment once, there is always a possibility of version-related errors in the future.
This time I used the pre-existing YOLO v8 models, but I’d like to change the models according to the targets I want to detect with the robot. I am also currently trying out annotation.