Trying Out Faster Whisper (Running on GPU, Python, and Node-RED)
Introduction
In this post, I tried performing transcription using Faster Whisper.
I had tried it before because it is faster than transcription with OpenAI's original Whisper, but at that time, I was running it on the CPU. Recently, I configured CUDA and PyTorch for YOLO to enable GPU usage, so I have now made it possible to use the GPU with Faster Whisper as well.
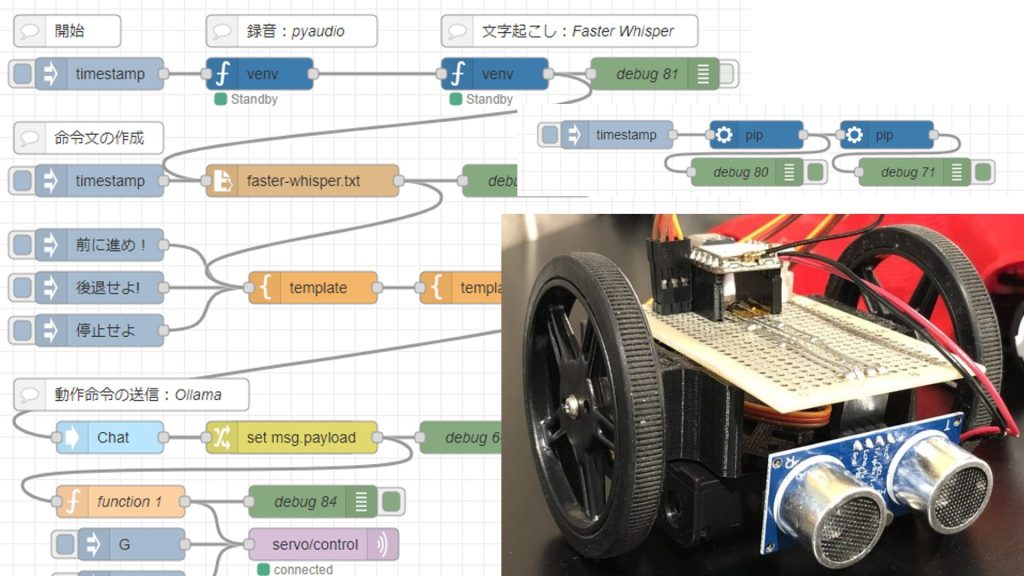
▼I have used it in this article as well. Previously, when the processing was slow, there were instances where the robot would not stop immediately.
▼Previous articles are here:
Setting Up the Environment
I am using Python 3.10 in a Windows 11 environment.
▼I am using a gaming laptop purchased for around 100,000 yen, running Windows 11.
Create a Python virtual environment and install the package using the following commands:
py -3.10 -m venv pyenv310
cd pyenv310
.\Scripts\activate
pip install faster-whisper▼It was installed without any particular issues.
▼I have summarized the creation of Python virtual environments in the following article:
Trying to Run on CPU
For the audio file to be transcribed, I used one generated by gTTS.
▼I have tried this in the following article:
▼I tried transcribing the following audio, which is about 9 seconds long.
▼It can be generated using the following flow:
[{"id":"35dcc8614a07234a","type":"inject","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"","props":[{"p":"payload"}],"repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"topic":"","payload":"Hello, this is a sample voice. May I help you? I can talk to you by voice. My interface will be further extended.","payloadType":"str","x":1830,"y":2760,"wires":[["5d52af097769c75c"]]},{"id":"64b94f8f700be65e","type":"venv-exec","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"gTTS","venvconfig":"36c2cf6f351fdc6e","mode":"execute","executable":"gtts-cli.exe","arguments":"","x":1970,"y":2820,"wires":[["1fd3d1f5c03a5732"]]},{"id":"1fd3d1f5c03a5732","type":"debug","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"debug 427","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"false","statusVal":"","statusType":"auto","x":2130,"y":2820,"wires":[]},{"id":"5d52af097769c75c","type":"template","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"","field":"payload","fieldType":"msg","format":"handlebars","syntax":"mustache","template":"'{{payload}}' --output voice.mp3","output":"str","x":1980,"y":2760,"wires":[["3dd3393f1f930dac","dee234e23e403bf1"]]},{"id":"3dd3393f1f930dac","type":"debug","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"debug 428","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"false","statusVal":"","statusType":"auto","x":2150,"y":2720,"wires":[]},{"id":"dee234e23e403bf1","type":"change","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"","rules":[{"t":"change","p":"payload","pt":"msg","from":"\"","fromt":"str","to":"","tot":"str"}],"action":"","property":"","from":"","to":"","reg":false,"x":2180,"y":2760,"wires":[["64b94f8f700be65e"]]},{"id":"36c2cf6f351fdc6e","type":"venv-config","venvname":"AI","version":"3.8"}]First, I will try the sample program from the documentation.
▼The Faster Whisper GitHub repository is here. It also contains information about model comparisons.
https://github.com/SYSTRAN/faster-whisper
The program adjusted for CPU is as follows. The audio file is named voice.mp3 and is placed in the directory of the Python virtual environment.
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel
model_size = "large-v3"
model = WhisperModel(model_size, device="cpu", compute_type="int8")
segments, info = model.transcribe("voice.mp3", beam_size=5)
print("Detected language '%s' with probability %f" % (info.language, info.language_probability))
for segment in segments:
print("[%.2fs -> %.2fs] %s" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))▼It seems the model needs to be downloaded for the first time.
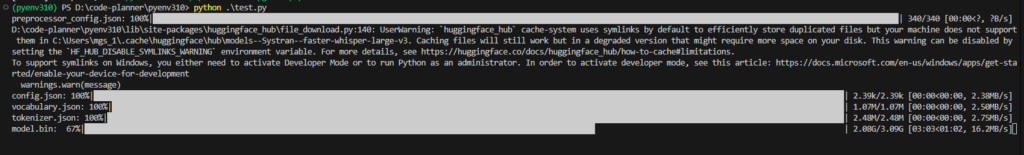
▼It ran successfully! Although the language was not specified, it was detected as "en".
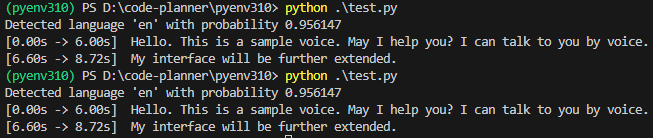
However, since the model is "large-v3", the processing is slow. It took about 30 seconds. Thinking that the language detection might also be taking time, I passed language="en" as an argument to transcribe.
segments, info = model.transcribe("voice.mp3", beam_size=5, language="en")▼It detected it as "en" with 100% probability. In this state, it took about 22 seconds.
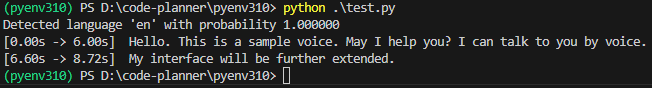
I tried changing the model from "large-v3" to others.
▼With "base", it could detect in about 2 seconds.
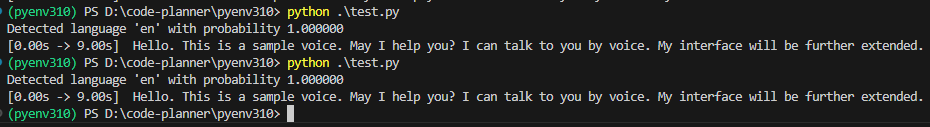
▼"tiny" was also about 2 seconds. Since "base" is also fast, there doesn't seem to be a difference for an audio file of this length.
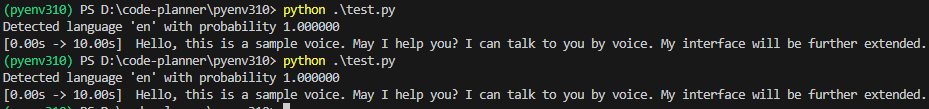
▼With "small", it took about 4 seconds.
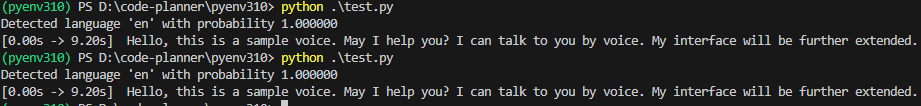
▼With "medium", it took about 10 seconds.
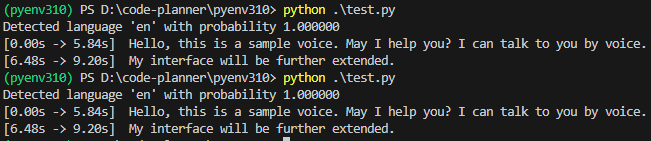
Perhaps because the audio was generated by gTTS, the detection accuracy did not particularly change.
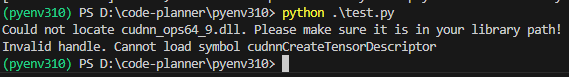
However, if I change the device of WhisperModel to "cuda", an error occurs.
▼The following error occurred:
Trying to Run on GPU
I will now resolve the error encountered when running on the GPU.
▼I previously encountered and resolved an error when trying to use YOLO on the GPU.
In the case of YOLO, I installed ultralytics in a Python virtual environment with CUDA 12.6, uninstalled torchvision once, and then reinstalled the torch-related packages.
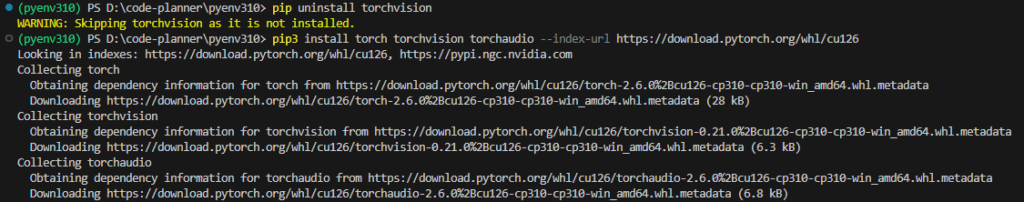
I tried the same procedure this time by executing the following commands:
pip uninstall torchvision
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126▼It seems torchvision was not installed to begin with. The packages were installed by the subsequent command.
After this, when I ran the following program, it worked.
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel
model_size = "large-v3"
model = WhisperModel(model_size, device="cuda", compute_type="int8")
segments, info = model.transcribe("voice.mp3", beam_size=5, language="en")
for segment in segments:
print("[%.2fs -> %.2fs] %s" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))▼It ran successfully! It took about 11 seconds with large-v3.
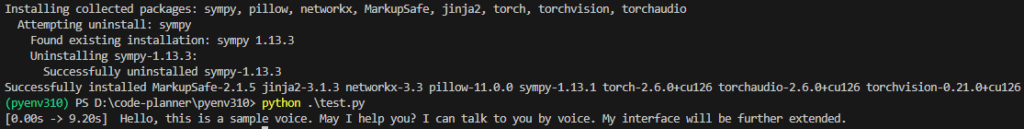
Compared to when running on the CPU, it seems to be faster when the model is large. Conversely, for smaller models, the CPU was faster.
▼It took about 4 seconds with "base". "tiny" was similar.

▼With "medium", it took about 10 seconds, which was about the same as with the CPU.
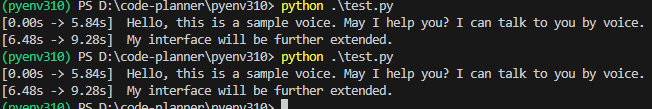
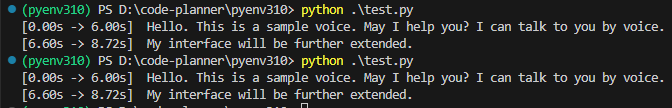
I tried setting the model to "large-v3" and changing the compute_type from "int8".
▼In the case of "float16", it took about 9.5 seconds.
▼In the case of "int8_float16", it was about 11 seconds.
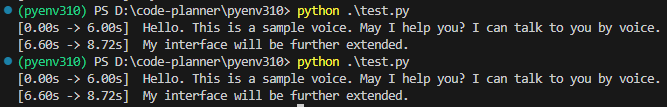
While float16 was slightly faster, I lack knowledge regarding the specific differences, so I intend to research this in more detail later.
Executing in Node-RED
I used Faster Whisper by utilizing the "python-venv" node I developed, which allows executing Python code in Node-RED.
▼I have written about the transition and mechanism of the "python-venv" node development in the following Qiita article:
https://qiita.com/background/items/d2e05e8d85427761a609
Based on the programs so far, I created the following flow.
▼The overall flow is here:
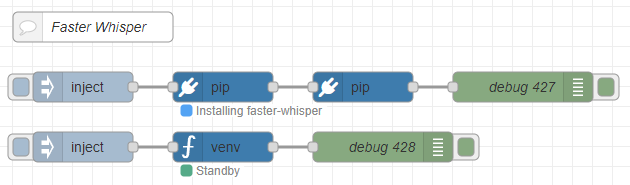
[{"id":"d34b1c24f210765d","type":"comment","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"Faster Whisper","info":"","x":1800,"y":2720,"wires":[]},{"id":"00832978f0f1b880","type":"pip","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","venvconfig":"6fee16ddf4b551d4","name":"","arg":"faster-whisper","action":"install","tail":false,"x":1930,"y":2780,"wires":[["cfb8692e8f555b75"]]},{"id":"bae2d94ba8963138","type":"inject","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"","props":[],"repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"topic":"","x":1790,"y":2780,"wires":[["00832978f0f1b880"]]},{"id":"b8890ca52996e4b4","type":"debug","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"debug 427","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"false","statusVal":"","statusType":"auto","x":2230,"y":2780,"wires":[]},{"id":"cfb8692e8f555b75","type":"pip","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","venvconfig":"6fee16ddf4b551d4","name":"","arg":"torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126","action":"install","tail":false,"x":2070,"y":2780,"wires":[["b8890ca52996e4b4"]]},{"id":"2fdbcc97e5a92ab2","type":"inject","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"","props":[{"p":"model","v":"large-v3","vt":"str"},{"p":"voice_path","v":"voice.mp3","vt":"str"}],"repeat":"","crontab":"","once":false,"onceDelay":0.1,"topic":"","x":1790,"y":2840,"wires":[["8b29ca988c0d3af3"]]},{"id":"045ca9bc4dc2d245","type":"debug","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","name":"debug 428","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"false","statusVal":"","statusType":"auto","x":2090,"y":2840,"wires":[]},{"id":"8b29ca988c0d3af3","type":"venv","z":"22eb2b8f4786695c","venvconfig":"6fee16ddf4b551d4","name":"","code":"from faster_whisper import WhisperModel\n\nmodel_size = msg['model']\nmodel = WhisperModel(model_size, device=\"cuda\", compute_type=\"float16\")\n\nsegments, info = model.transcribe(msg['voice_path'], beam_size=5, language=\"en\")\n\nfor segment in segments:\n print(\"[%.2fs -> %.2fs] %s\" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))","continuous":false,"x":1930,"y":2840,"wires":[["045ca9bc4dc2d245"]]},{"id":"6fee16ddf4b551d4","type":"venv-config","venvname":"FasterWhisper","version":"3.10"}]It is set up to install faster-whisper and torch-related packages using the "pip" node.
You can execute Python code in the "venv" node.
▼I wrote the code as follows:
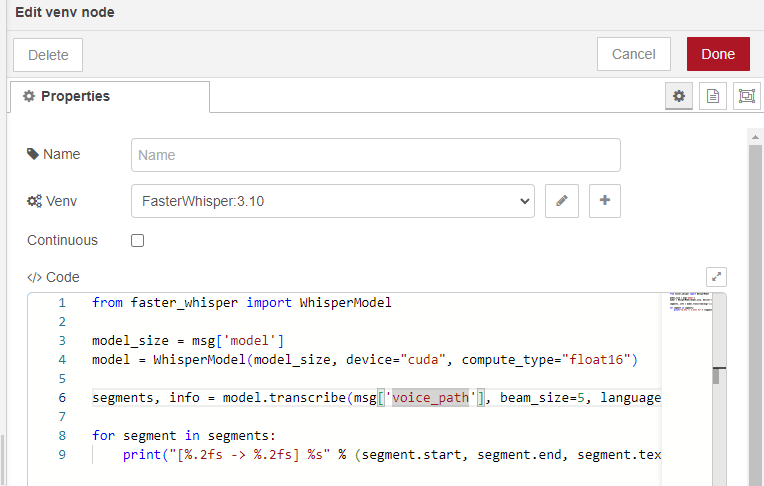
The notation msg['model'] is unique to this node and allows it to receive Node-RED messages.
▼It is specified in the "inject" node as follows:
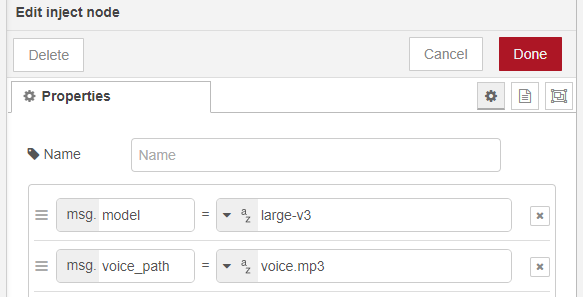
I tried running it with the device set to "cuda".
▼It ran successfully on the GPU!
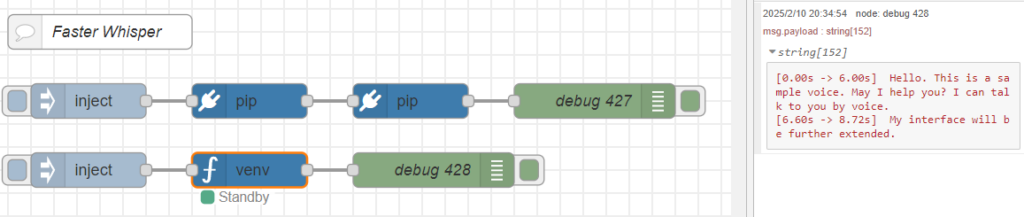
Since I was able to execute it with the "python-venv" node, it seems possible to combine it with other nodes.
Finally
I compared the processing speeds and found that the GPU was faster for larger model sizes. The CPU was also sufficiently fast, taking about 2 seconds with the "base" model. Since this was a short audio of about 9 seconds, it might change with longer audio. Also, perhaps because the audio was generated by gTTS, the transcription results did not particularly change. The accuracy might vary with human voices. I would like to check the accuracy while enabling actual dialogue with a robot.